It’s been six years since World IPv6 Launch day on the 6th June 2012. In those six years we’ve managed to place ever increasing pressure on the dwindling pools of available IPv4 addresses, but we have still been unable to complete the transition to an all-IPv6 Internet. Nobody predicted this situation when we first thought about the consequences of running out of IPv4 addresses. We all thought that the depletion of IPv4 addresses would in a continuously expanding Internet provide sufficient rationale for IPv6. We have been proved right that growth of the Internet has been inexorable. Personal computers have jumped from the desk to our pockets, and then leapt across to a world of managed devices. A census of the Internet’s connected devices would readily number in the tens of billions of devices. If they all needed a globally unique permanent IP address IPv6 would’ve been an imperative over a decade ago. But that simply has not happened. Instead, we’ve managed to completely redesign the architecture of the Internet. Some might suggest we have undertaken this effort simply to avoid the transition to IPv6. Perhaps that a bit of an extreme view, but the picture of IPv6 today is certainly puzzling. What’s going on? Data would help answer this question, and at APNIC, we’ve been performing a large-scale Internet-wide measurement of the level of adoption of IPv6 since late 2011.
I won’t repeat the details of the measurement system here, but you can find a description of the way we undertake this measurement in a 2017 presentation “How we measure IPv6“.
At APNIC we operate the measurement system using a sample rate of between 6 to 10 million endpoints per day, drawn from across most of the deployed Internet. We are able to analyse this data to produce a time series of the adoption of IPv6 over time. The overall picture of the adoption of IPv6 by Internet users since late 2011 is shown in Figure 1.
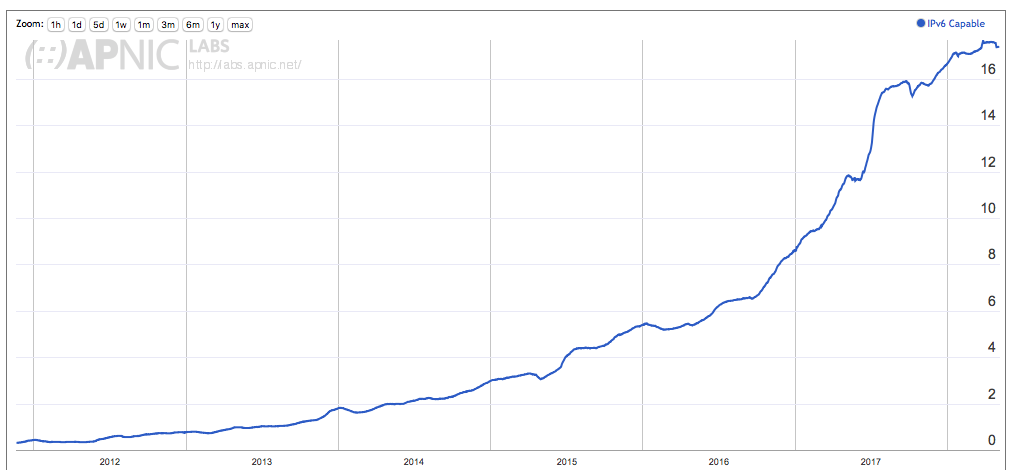
Figure 1 – User Adoption of IPv6 (percentage of total user population)
When these measurements commenced in late 2011 there was very little in the way of IPv6 deployment, and the total deployment level was measured at 0.3% of the internet user base at the time (i.e., an average of 1 in 300 users could successfully use IPv6 to access a web object).
World IPv6 Launch day on the 6th June 2012 saw the rate of IPv6 adoption rise from 0.4% to 0.8% on the day, but the long term IPv6 adoption rate was still very slow. It was not until mid-2013 that we saw the Internet-wide IPv6 adoption rise above 1%. A major change in the IPv6 deployment picture occurred over the two-and-a-half-year period from the start of 2015 to mid 2017. Over that period the level of IPv6 adoption rose from 3% to 15%, and the majority of that rise occurred in the first half of 2017. By the end of 2017 the level of IPv6 deployment was measured at some 18% of the Internet, but there has been no significant further movement in that number across the first four months of 2018. Just four months is probably an insufficient period to justify an assertion that IPv6 deployment has stalled, but the hiatus in the growth of the use of IPv6 is certainly a source of some concern (Figure 2).
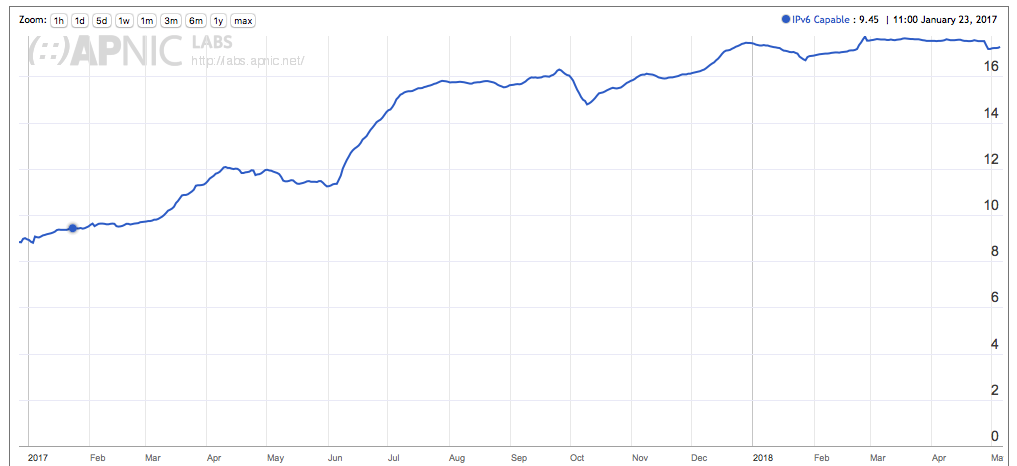
Figure 2 – User Adoption of IPv6: 2017 to mid-2018
Can we determine what factors might lie behind this recent slowdown in the growth of IPv6? Perhaps some pointers to an answer to this question lie in an examination of the opposite question. What are the common factors that have been behind the deployment of IPv6 in networks so far?
In this article I’d like to look at some potential answers to this question and see if the accumulated data can support any of these theories.
Who Uses the IPv6 Internet?
To start with it might be instructive to look at the Internet itself, and in particular look at the national populations of Internet users. Where are the Internet’s users?
One resource I’ve been using is “Internet Live Stats” which provides an estimate of the total population of Internet users per economy.
Today the five largest national pools of Internet users are in China, India, the United States, Brazil and Japan. Together these five economies account for slightly more than one half of the entire current estimate of some 3.4 billion Internet users. In terms of IPv6 adoption, it follows that if all of these five economies undertook a close to ubiquitous deployment of IPv6 they would be able to swing the IPv6 adoption measurement point to over one half of all users. Obviously, this is yet to happen and the actual picture of IPv6 deployment is somewhat different. The most overt missing element at this national level in this set of the five largest national Internet user pools is China, where visible IPv6 deployment is yet to lift above relatively small levels of adoption.
If these existing IPv6 users are not in China, then where are they? Of the estimated 513 million IPv6 users, let’s look at the subset of economies where the national IPv6 user population is at least 3 million, or more than 1% of the total IPv6 user population (Table 1).
|
Country |
IPv6 Users |
% of Total World Count | % of National Users |
|
India
|
242M | 44% | 52% |
|
USA
|
117M | 21% | 40% |
|
Germany
|
30M | 6% | 42% |
|
Brazil
|
30M | 6% | 21% |
|
Japan
|
28M | 5% | 24% |
|
UK
|
17M | 3% | 27% |
|
France
|
12M | 2% | 21% |
|
Canada
|
7M | 1% | 20% |
|
Belgium
|
6M | 1% | 58% |
|
Malaysia
|
5M | 1% | 22% |
|
Rep. of Korea
|
5M | 1% | 11% |
|
Vietnam
|
4M | 1% | 8% |
|
Australia
|
3M | 1% | 16% |
Table 1 – IPv6 Users per Economy
The economy with the highest IPv6 adoption level is Belgium. Other countries which high IPv6 deployment levels do not have a large population of Internet users in absolute terms, so missing from Table 1 are Greece (37%), Switzerland (34%), Luxembourg (33%) Uruguay (32%) and Portugal (25%). This table might also suggest that within each economy the distribution of IPv6 users is uniform across all national ISPs. This is definitely not the case, and to sharpen our focus in looking at where IPv6 is deployed, we need to look at each Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Table 2 shows the 20 ISPs with the largest estimated IPv6 user populations.
|
Rank
|
AS
|
AS Name
|
CC
|
Users (est) | V6 Users (est) | V6% |
|
1
|
AS55836
|
Reliance Jio
|
IN
|
257,116,163 | 236,669,761 | 92% |
|
2
|
AS7922
|
Comcast Cable
|
US
|
48,845,229 | 35,701,856 | 73% |
|
3
|
AS7018
|
ATT Services
|
US
|
27,190,530 | 21,621,772 | 80% |
|
4
|
AS38266
|
Vodafone Essar Ltd.,
|
IN
|
42,711,918 | 17,068,044 | 40% |
|
5
|
AS22394
|
Verizon Wireless
|
US
|
18,499,350 | 15,788,328 | 85% |
|
6
|
AS45271
|
Idea Cellular
|
IN
|
38,817,216 | 15,470,268 | 40% |
|
7
|
AS21928
|
T-Mobile USA
|
US
|
15,402,964 | 14,513,144 | 94% |
|
8
|
AS3320
|
Deutsche Telekom ISP
|
DE
|
23,392,392 | 14,118,853 | 60% |
|
9
|
AS5607
|
BSKYB Broadband
|
GB
|
13,714,642 | 12,821,973 | 93% |
|
10
|
AS2516
|
KDDI
|
JP
|
22,146,612 | 11,725,651 | 53% |
|
11
|
AS28573
|
CLARO
|
BR
|
24,184,316 | 11,048,081 | 46% |
|
12
|
AS17676
|
Softbank BB
|
JP
|
25,292,851 | 8,259,099 | 33% |
|
13
|
AS3215
|
Orange
|
FR
|
16,990,645 | 7,976,416 | 47% |
|
14
|
AS20057
|
ATT Mobility
|
US
|
14,455,761 | 7,967,862 | 55% |
|
15
|
AS22773
|
Cox Communications
|
US
|
11,537,814 | 6,224,326 | 54% |
|
16
|
AS18881
|
Telfonica Brasil
|
BR
|
14,125,727 | 5,844,652 | 41% |
|
17
|
AS10507
|
Sprint PCS
|
US
|
7,548,658 | 5,797,873 | 77% |
|
18
|
AS9644
|
SK Telecom
|
KR
|
6,912,564 | 5,654,940 | 82% |
|
19
|
AS4713
|
OCN NTT
|
JP
|
19,995,028 | 5,586,165 | 28% |
|
20
|
AS31334
|
KabelDeutschland
|
DE
|
7,456,144 | 5,340,966 | 72% |
Table 2 – IPv6 Users per ISP.
Three surprising numbers in this table are those of 94% adoption in T-Mobile USA, 93% in BSkyB and 92% in Reliance Jio. They are surprising in that prior to these deployments we had though that an ISP deployment of IPv6 was only a part of the story. It was up to the connected user network to also use IPv6-capable equipment within their edge network. The Comcast deployment level of 73% reflects this, in that while the ISP network is fully deployed with IPv6 support, there are is still IPv4-only customer equipment in use. Upgrading equipment in the home or office takes time, and the 73% adoption level reflects this. Why can these three networks achieve significantly higher levels of IPv6 adoption? I suspect that this is a reflection of the difference between Mobile ISPs and fixed infrastructure of mixed ISPs, and even the dual stack technology used by the mobile ISP. T-Mobile USA uses 464-XLAT, where the communications system is an IPv6-only network, and all attached devices use IPv6 to connect to the network. IPv4 is a tunnelled addition, where the IPv4 module is found in the user device. When given the choice these devices have a very strong affinity to use IPv6 over IPv4. It would not be surprising to learn that a similar approach was taken in Reliance Jio and BSkyB.
However, these three ISPs are somewhat anomalous within the larger picture of per-ISP deployment, and it is more common to observe that within an ISP, IPv6 is not ubiquitously used by customer equipment. Within these 20 ISPs with the largest numbers of IPv6 users, we see a variation of IPv6 penetration between a low of 28% deployment (NTT in Japan) to 94% (T-Mobile USA). It is likely that the lower numbers reflect an ISP that has integrated a number of different consumer products into a single AS, and only some of the products have integrated IPv6 support as yet, or the numbers reflect a combination of customer equipment capability overlayed on the ISP’s network IPv6 capabilities.
The basic observation is that IPv6 deployment is by no means uniform, and deployment levels are variable within an individual economy and even within an individual ISP. The question now is: Are there common factors behind these IPv6 deployments?
Theories of IPv6 Deployment
Let’s look at the available data about the Internet, its users and ISPs to see if there is some visible correlation between IPv6 deployment in the ISP and some other factor that we can measure. What we are looking for here is some evidence that IPv6 deployment and some factor are closely related.
IPv6 is only for the Rich
It’s not strictly necessary for an ISP to deploy IPv6 in order to provide a consumer Internet access product. There are apparently no significant services that are accessible only using IPv6, and as long as an ISP has sufficient public IPv4 addresses to service the activities of its customer base, then it is not forced to deploy IPv6. From this admittedly very limited perspective the case could be made that IPv6 is a “luxury” activity, as distinct from an “essential” activity.
But is this the case? Is IPv6 an activity that is undertaken only by those ISPs who can afford to undertake an activity that is not strictly speaking absolutely required? Or, to put it more bluntly, is IPv6 only for the rich ISPs?
One way to measure the ‘wealth’ of an ISP is to look at the aggregate net wealth of its customer base. Using the current Gross Domestic Product of each national economy, and the current national population estimates we can derive a GDP per capita for each economy. We can then use the estimate of the customer size of each ISP to derive a notional ‘wealth’ value by multiplying this customer size by the GDP per capita. The 20 “richest” ISPs using this method are shown in Table 3.
The IPv6 deployment figures from these 20 ISPs show a range of IPv6 uptake from 0% through to 94%. Some 13 of these 20 ISPs have an IPv6 deployment above 35%. While 3 of the low-level IPv6 use ISPs are Chinese, there are also Korean, US and UK ISPs in a similar position. The proposition that IPv6 is only adopted by “richer” ISPs is looking like a somewhat tenuous proposition these days.
|
Rank
|
AS
|
AS Name
|
CC
|
Users (est) | Value (est) | IPv6 Users | IPv6% |
|
1
|
AS7922
|
Comcast Cable
|
US
|
48,845,229 | 2,783,982,672,084 | 35,701,856 | 73% |
|
2
|
AS4134
|
ChinaNet
|
CN
|
310,853,595 | 2,460,095,350,830 | 244,673 | 0% |
|
3
|
AS7018
|
ATT Services
|
US
|
27,190,530 | 1,549,751,447,880 | 21,621,772 | 80% |
|
4
|
AS4837
|
China Unicom
|
CN
|
161,782,709 | 1,280,348,359,026 | 109,825 | 0% |
|
5
|
AS22394
|
Verizon Wireless
|
US
|
18,499,350 | 1,054,388,952,600 | 15,788,328 | 85% |
|
6
|
AS3320
|
Deutsche Telekom
|
DE
|
23,392,392 | 988,562,485,920 | 14,118,853 | 60% |
|
7
|
AS17676
|
Softbank BB
|
JP
|
25,292,851 | 984,220,710,963 | 8,259,099 | 33% |
|
8
|
AS21928
|
T-Mobile USA
|
US
|
15,402,964 | 877,907,336,144 | 14,513,144 | 94% |
|
9
|
AS2516
|
KDDI
|
JP
|
22,146,612 | 861,791,112,756 | 11,725,651 | 53% |
|
10
|
AS20115
|
Charter Comms
|
US
|
14,901,389 | 849,319,567,444 | 1,528,640 | 10% |
|
11
|
AS20057
|
ATT Mobility
|
US
|
14,455,761 | 823,920,553,956 | 7,967,862 | 55% |
|
12
|
AS4713
|
OCN NTT
|
JP
|
19,995,028 | 778,066,524,564 | 5,586,165 | 28% |
|
13
|
AS22773
|
Cox Communications
|
US
|
11,537,814 | 657,609,246,744 | 6,224,326 | 54% |
|
14
|
AS3215
|
Orange
|
FR
|
16,990,645 | 642,144,437,130 | 7,976,416 | 47% |
|
15
|
AS701
|
Verizon Business
|
US
|
11,056,076 | 630,152,107,696 | 62,472 | 1% |
|
16
|
AS209
|
CenturyLink
|
US
|
9,668,638 | 551,073,691,448 | 24,719 | 0% |
|
17
|
AS5607
|
BSKYB
|
GB
|
13,714,642 | 546,089,615,156 | 12,821,973 | 93% |
|
18
|
AS5089
|
NTL
|
GB
|
13,230,998 | 526,831,878,364 | 967 | 0% |
|
19
|
AS9808
|
Guangdong Mobile
|
CN
|
59,428,828 | 470,319,744,792 | 17,133 | 0% |
|
20
|
AS4766
|
Korea Telecom
|
KR
|
16,463,111 | 454,085,527,602 | 385,156 | 2% |
Table 3 – Top 20 ISPs as valued by GDP per capita.
Another way to look at this data is by using a scatter plot, comparing the IPv6 deployment level on one axis and the aggregate value of the ISP’s customer base on the other. This comparison is shown for the same 20 ISPs in Figure 3 using a scatter plot.
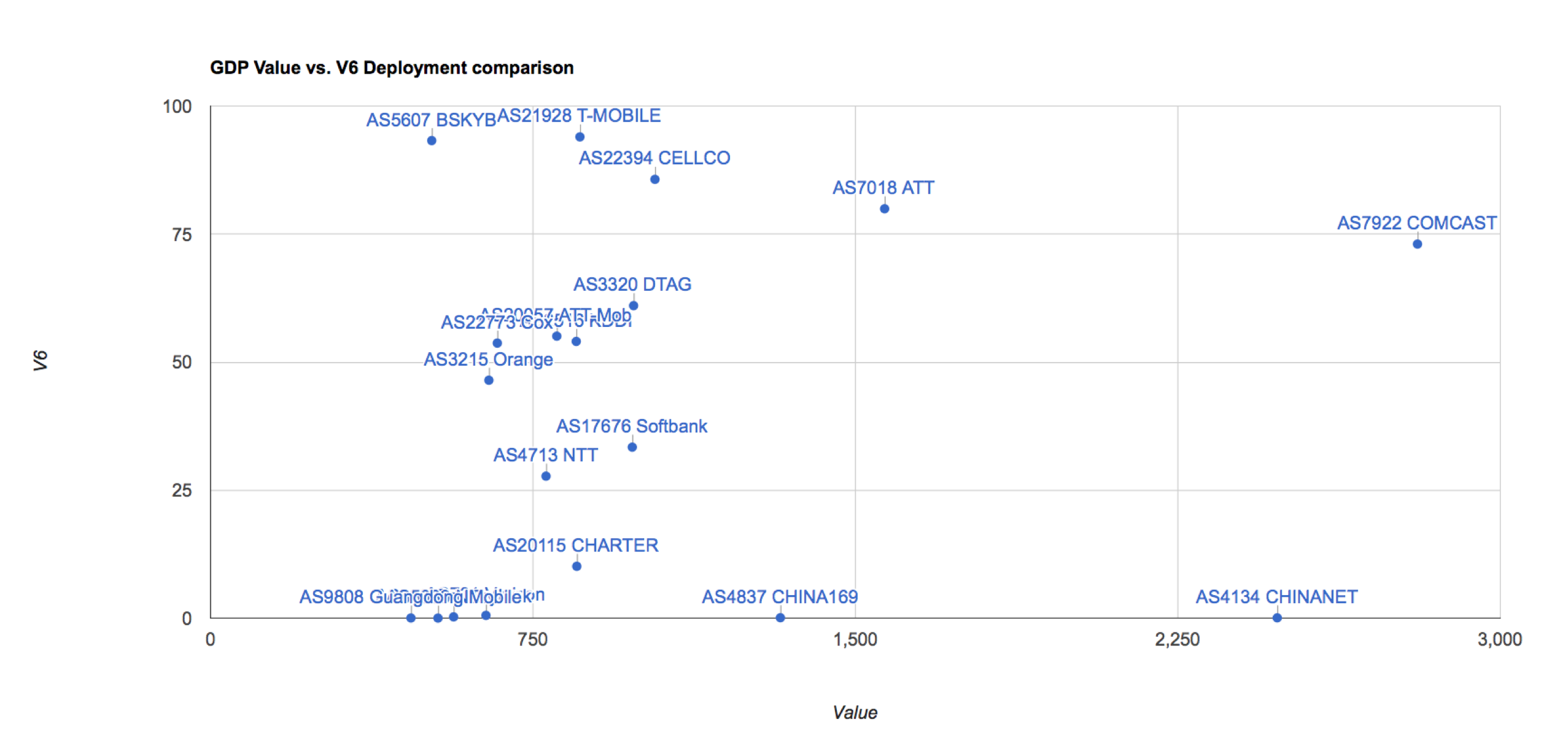
Figure 3 – IPv6 Deployment vs ISP Customer value for 20 richest ISPs
If there were a clear relationship, then we should see a clustering of the data into some band where higher levels of notional value of the ISP would correlate with higher levels of IPv6 deployment. Clearly no such clustering is evident in these numbers. It is also the case that the 20 richest ISPs do not contain the majority of the IPv6 user population. Some of the larger IPv6 deployments, such as Reliance Jio in India and Claro in Brazil fall outside this top 20. The top 20 richest ISPs only contain a little over one quarter of the IPv6 user base, while the other three quarters of the Internet’s IPv6 users are served from ISPs outside this same top 20 rich ISP list. If we take the 400 highest value ISPs and perform the same comparison of value against IPv6 deployment, the correlation between the two metrics is shown in Figure 4.
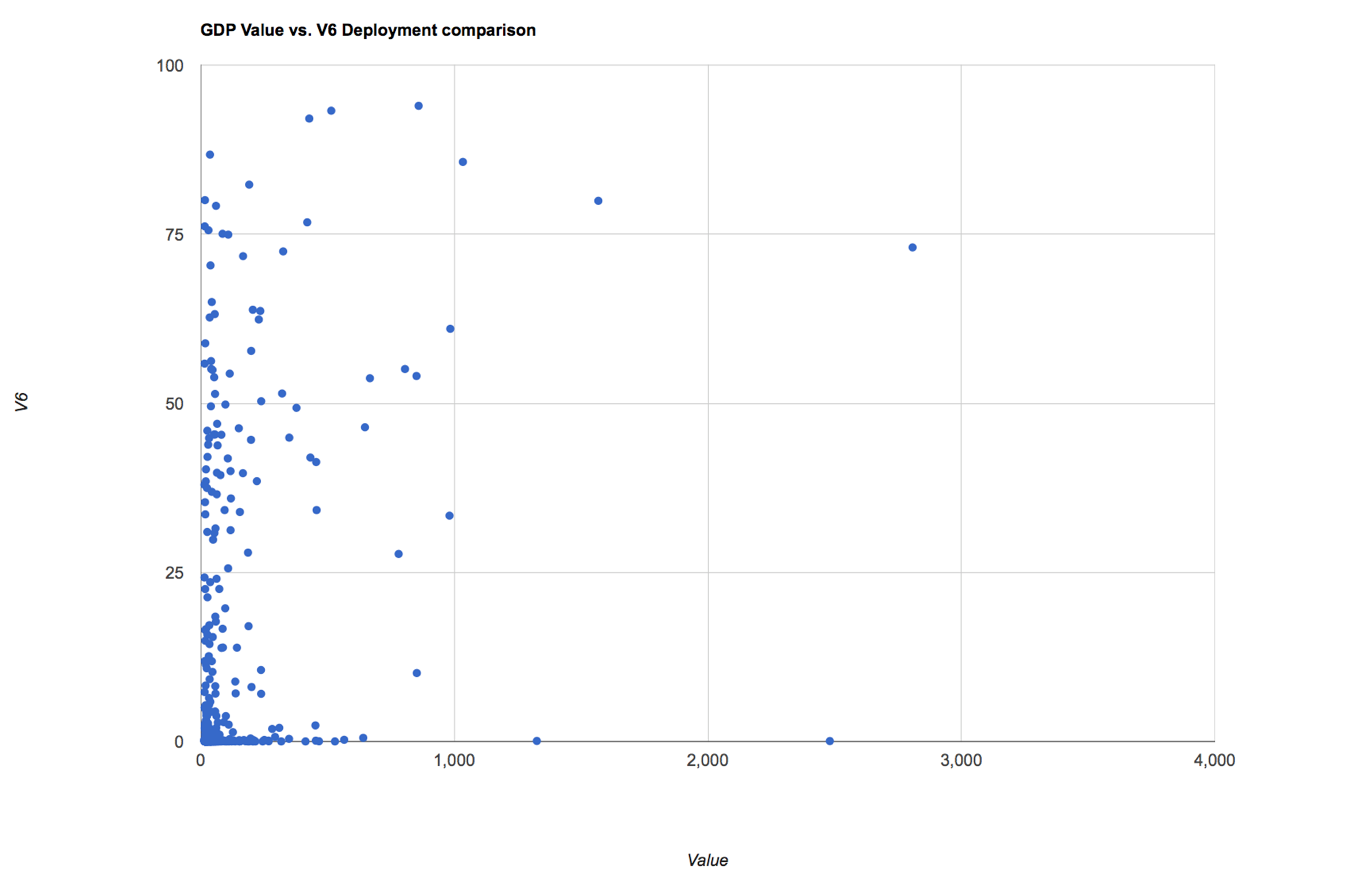
Figure 4 – IPv6 Deployment vs ISP Customer value for 400 richest ISPs
Within this larger data set here is still no clear correlation, and while having access to funding to deploy IPv6 is obviously an advantage, it is clear that ISPs that serve all profiles of user populations have decided to adopt IPv6.
It seems that the data is saying that you don’t necessarily need to be an ISP for a wealthy and large base of customers to afford to deploy IPv6. Being rich may well help to support the IPv6 business case, but it’s not a strict precondition here.
IPv6 is deployed when the ISP is growing rapidly
Another potential motivation for IPv6 deployment is the scenario where the ISP is experiencing a rapid growth in customer numbers. In this scenario it may be the case that the ISP has not made sufficient provision in its IPv4 holdings for this growth and needs to find a workable solution. Using the IPv4 address market to obtain additional IPv4 address is the obvious approach and many ISPs have used this market to obtain more IPv4 addresses, but the approach is not without its associated cost. While IPv6 is not backward compatible with IPv4 and is not directly substitutable for a lack of IPv4 addresses, IPv6 deployment can ease the pressure on an ISP’s IPv4 address pools. Dual-stack hosts on a dual-stack network typically use a “happy eyeballs” approach, where an IPv6 connection is attempted first, and IPv4 is used only if the IPv6 connection does not complete in time. This means that a dual stack deployment will push usage to IPv6 as long as the users access services from sites also using IPv6. A rapidly growing ISP may well see part of a response to such rapid growth in the deployment of IPv6. The Reliance JIO network appears to be a good example of this approach.
How general is this scenario? If we could identify those ISPs who are experiencing the largest growth levels in recent months would we see a strong correlation with that ISP’s adoption of IPv6? Table 4 shows the 20 large (more than 1M customers) who have experienced the highest growth rates over the past 16 months.
Only 7 of these rapidly expanding ISPs have an IPv6 deployment greater than 10%. Of these ISP who have deployed IPv6 to this level, all are expanding their IPv6 deployment at rates even greater than the underlying ISP growth rate. It appears to indicate that where an ISP has commenced an IPv6 deployment, growth in the underlying customer base is accompanied by an even faster growth in the IPv6 deployment levels. But at the same time where there is no initial IPv6 deployment the rapid growth of an ISP’s customer base does not appear to act as an incentive for IPv6 deployment.
|
Rank
|
AS
|
AS Name
|
CC
|
Users (5/18) | Users (1/17) | Growth | V6% | V6 Growth |
|
1
|
AS9644
|
SK Telecom
|
KR
|
6,846,142 | 1,521,612 | 350% | 81% | 55% |
|
2
|
AS131445
|
Advance Wireless
|
TH
|
4,657,758 | 1,047,844 | 345% | 42% | 42% |
|
3
|
AS37075
|
ZAIN UG
|
UG
|
3,776,883 | 1,021,996 | 270% | 0% | 0% |
|
4
|
AS45271
|
Idea Cellular
|
IN
|
38,917,738 | 11,901,462 | 227% | 39% | 33% |
|
5
|
AS9605
|
NTT DOCOMO
|
JP
|
5,840,898 | 1,826,417 | 220% | 8% | 8% |
|
6
|
AS55836
|
Reliance Jio
|
IN
|
252,882,243 | 79,115,818 | 220% | 92% | 19% |
|
7
|
AS56048
|
China Mobile
|
CN
|
4,632,749 | 1,479,558 | 213% | 0% | 0% |
|
8
|
AS132061
|
Realmove
|
TH
|
3,033,271 | 1,035,635 | 193% | 0% | 0% |
|
9
|
AS56041
|
China Mobile Zhejiang
|
CN
|
21,567,119 | 7,379,958 | 192% | 0% | 0% |
|
10
|
AS38266
|
Vodafone Essar
|
IN
|
41,404,353 | 14,332,740 | 189% | 40% | 40% |
|
11
|
AS21928
|
T-Mobile USA
|
US
|
15,522,746 | 5,725,701 | 171% | 94% | 17% |
|
12
|
AS4761
|
INDOSAT
|
ID
|
7,750,603 | 2,889,955 | 168% | 0% | 0% |
|
13
|
AS56047
|
China Mobile Hunan
|
CN
|
6,839,156 | 2,579,417 | 165% | 0% | 0% |
|
14
|
AS10507
|
Sprint PCS
|
US
|
7,582,025 | 2,936,890 | 158% | 77% | 49% |
|
15
|
AS24389
|
GrameenPhone
|
BD
|
5,202,927 | 2,018,349 | 158% | 0% | 0% |
|
16
|
AS197207
|
MCCI
|
IR
|
7,451,173 | 2,897,240 | 157% | 0% | 0% |
|
17
|
AS33771
|
SAFARICOM
|
KE
|
10,556,969 | 4,199,062 | 151% | 2% | 2% |
|
18
|
AS23693
|
Telekomunikasi Selular
|
ID
|
15,027,678 | 6,043,987 | 149% | 0% | 0% |
|
19
|
AS15897
|
VODAFONE TURKEY
|
TR
|
4,079,685 | 1,653,584 | 147% | 0% | 0% |
|
20
|
AS5410
|
BOUYGTEL-ISP
|
FR
|
7,359,006 | 3,015,444 | 144% | 2% | 2% |
Table 4 – Top 20 ISPs ranked by customer growth.
We can look at the correlation between the underlying growth in the customer base and the growth in IPv6 deployment for the 400 most rapidly growing ISPs (Figure 5).

Figure 5 – IPv6 Deployment vs ISP growth value for 400 growing ISPs
Once more there is no clear correlation going on here. One sub-group of ISPs with growth rates between 10% and 210% show V6 deployment level that rises as the ISP growth rises (as shown by the blue group in Figure 5), but a second group shows a constant level of around 40% IPv6 deployment for all growth rates between 2% and 350% (orange group). The majority of the data points are in the band where IPv6 deployment is less than 20% and growth spans 2% through to 280% (green group).
Once more, we cannot substantiate this theory from the available data. A rapidly expanding ISPs does not necessarily deploy IPv6 as a response to this rapid growth. Some ISPs do, but many others do not.
IPv6 is deployed when an ISP runs out of IPv4 Addresses
The development of the IPv6 protocol was a response to the projection of IPv4 address exhaustion. The rationale was that an operator would be strongly motivated to deploy IPv6 in order to avoid many of the issues of attempting to operate an IP service with insufficient IP addresses.
If this is the case, then we should be able to look at each ISP and estimate their level of IPv4 address scarcity and observe that those ISPs with the greatest level of address scarcity pressure also showing substantial deployment of IPv6.
Table 4 shows the Internet’s 20 largest ISPs as measured by the estimated size of their customer base. For each of these ISPs we’ve compared the number of users to the total span of advertised IPv4 addresses that are announced by this ISP. This gives us a notional value of the number of users for each visible public IPv4 address. The largest values, indicating the most extreme levels of IPv4 public address scarcity are seen Nigeria, and the largest ISP in that country has ratio of 402 customers per public IPv4 address. Three of the Indian ISPs have ratios of 66 or greater.
The question is whether the higher the ratio of customers for each IPv4 address relates to deployment of IPv6 in that ISP. There are 10 ISPs in this list with an IPv6 deployment level of above 10%, but the address use ratios of these 10 vary from 0.34 (or 3 addresses per customer) to 70 customers per IP address.
|
Rank
|
AS
|
AS Name
|
CC
|
Users (est) | IPv4 Addrs | IPv4 Ratio | IPv6% |
|
1
|
AS4134
|
ChinaNET
|
CN
|
309,309,607 | 108,180,224 | 2.86 | 0% |
|
2
|
AS55836
|
Reliance Jio
|
IN
|
252,882,243 | 3,593,728 | 70.37 | 92% |
|
3
|
AS4837
|
China Unicom
|
CN
|
157,000,163 | 56,262,655 | 2.79 | 0% |
|
4
|
AS45609
|
Bharti Airtel
|
IN
|
70,522,541 | 3,968,000 | 17.77 | 4% |
|
5
|
AS9808
|
Guangdong Mobile
|
CN
|
61,231,552 | 18,678,528 | 3.28 | 0% |
|
6
|
AS7922
|
Comcast
|
US
|
48,758,165 | 71,069,952 | 0.69 | 73% |
|
7
|
AS38266
|
Vodafone Essar
|
IN
|
41,404,353 | 601,344 | 68.85 | 40% |
|
8
|
AS45271
|
Idea Cellular
|
IN
|
38,917,738 | 584,448 | 66.59 | 39% |
|
9
|
AS4812
|
China Telecom
|
CN
|
35,767,235 | 8,605,952 | 4.16 | 0% |
|
10
|
AS29465
|
VCG-AS
|
NG
|
32,523,737 | 80,896 | 402.04 | 0% |
|
11
|
AS8151
|
Uninet S.A. de C.V.
|
MX
|
29,853,671 | 13,798,112 | 2.16 | 11% |
|
12
|
AS4808
|
China Unicom Beijing
|
CN
|
28,340,473 | 6,860,287 | 4.13 | 0% |
|
13
|
AS7018
|
ATT
|
US
|
27,078,307 | 80,679,680 | 0.34 | 79% |
|
14
|
AS17676
|
Softbank BB
|
JP
|
25,227,427 | 44,918,528 | 0.56 | 33% |
|
15
|
AS28573
|
CLARO S.A.
|
BR
|
24,281,752 | 9,138,176 | 2.66 | 47% |
|
16
|
AS3320
|
Deutsche Telekom
|
DE
|
23,467,950 | 34,140,416 | 0.69 | 60% |
|
17
|
AS8452
|
Telecom Egypt
|
EG
|
23,396,481 | 7,063,040 | 3.31 | 0% |
|
18
|
AS9121
|
Turk Telecom
|
TR
|
22,621,162 | 6,905,600 | 3.28 | 0% |
|
19
|
AS2516
|
KDDI
|
JP
|
22,149,880 | 18,765,568 | 1.18 | 53% |
|
20
|
AS56041
|
China Mobile Zhejiang
|
CN
|
21,567,119 | 2,939,904 | 7.34 | 0% |
Table 5 – Top 20 ISPs ranked by estimated customer size, and IPv4 Use Ratio
The table does not show a clear correlation, but once more we can take the largest 400 ISPs and use a scatter plot to match their IPv4 “use ratio” (the number of customers per advertised IPv4 address) to the Ipv6 deployment level. This is shown in Figure 6.
Most of these ISPs have IPv4 address use ratios of between 0.5 (or, inversely, 2 addresses per estimated customer) and 10 (i.e. 10 customers per advertised IP address). However, there is no visible relationship between this IPv4 address use ratio and IPv6 deployment. The highest customer to IPv4 address ratios are in excess of 800, experienced by a number of ISPs in Nigeria, yet there is no visible level of IPv6 deployment in those ISPs as yet.
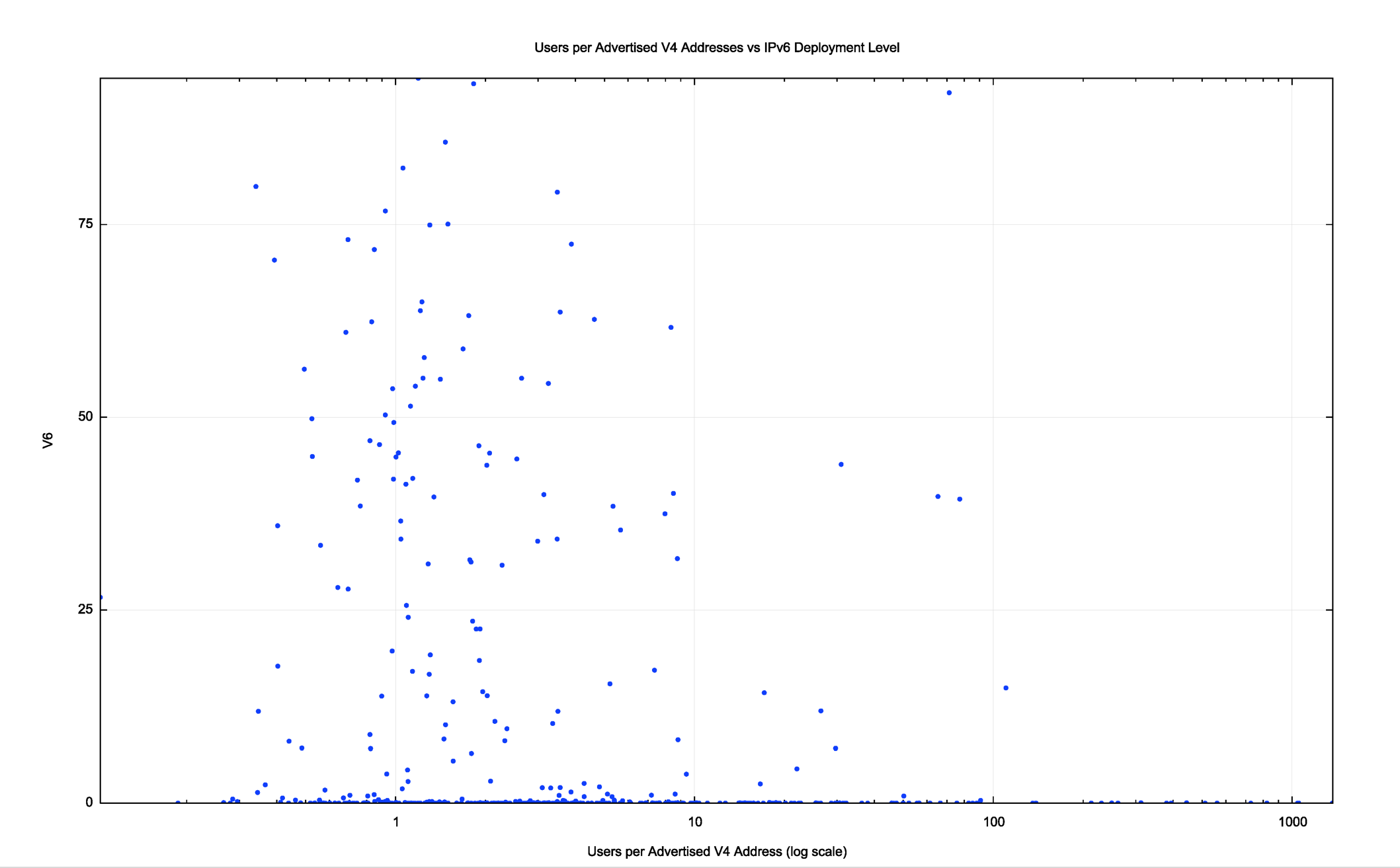
Figure 6 – IPv6 Deployment vs IPv4 Address Use
This is perhaps the most surprising result. The motivation behind the timing of the development of the IPv6 protocol was to have a mature and well understood technology platform long before we ran down the levels of IPv4 to the extent that not only are the pools completely exhausted. But instead of deploying IPv6, many ISPs are deploying address sharing technologies.
There are good reasons why many ISPs have taken this path as a short-term business response. For many ISPs an investment in IPv6 does not offer immediate benefits to the ISP customer base. It does not reduce the ISP’s cost base, and if development funds are finite it is not unsurprising that many ISPs have chosen to concentrate on activities that offer direct outcomes, such as 5G in the mobile sector, or securing content arrangements in broadband service sector. IPv6 is often seen as a risk mitigation measure, and while address sharing technologies are capable of deferring the problem, IPv6 is not screaming for an operator’s attention in many cases. However, perceptions of risk can be very subjective, and while some ISPs are comfortable with deferring IPv6 deployment, others have already taken steps. The salient observation here is that the level of address shortage being experienced by an ISP does not appear to have a strong influence on the perception of risk of a collapse of the IPv4 Internet.
IPv6 is deployed when an ISP’s competitors deploy IPv6
The early days of the outreach of the Internet from the academic and research sector were seen as wild days! The industry was driven by entrepreneurs who saw a unique opportunity in challenging the entrenched monopoly of the telephone companies. The catchcry of the time was innovation and a deliberate effort to distinguish these new entrants as being completely different from the ponderous conservatism of the telephone industry.
Inevitably size creates inertia, and as the customer base of these service providers expanded their ability to move quickly was significantly reduced. The Internet business sector now shows behaviours that have much in common with the old telephone sector. One of the common characteristics in this form of environment is that the dominant operators in a market tend to act in similar ways, offering similar services and at similar prices to their customers.
What happens when one of the larger service providers in a market offers a new service? It is often the case that this provides sufficient impetus for other providers in the same market to offer the same service.
Does this same behaviour apply to IPv6? How many national markets exist where three or more of the six largest ISPs have IPv6 deployment of 20% or more? The list is surprisingly small, as shown in Table 6.
| Economy | IPv6 |
|---|---|
|
India |
58% |
|
Belgium |
58% |
|
USA |
44% |
|
Germany |
39% |
|
Greece |
38% |
|
Japan |
27% |
|
Brazil |
26% |
Table 6 – Countries with Combined IPv6 Deployment
The other more populous economies with significant level of IPv6 deployment only have 2 or 1 of the largest 6 ISPs providing IPv6 services to their customers.
Does this small list of economies in Table 6 prove or disprove the theory that competitive pressures tend to push other ISPs to deploy IPv6 once IPv6 deployment has commenced in an economy? It’s hard to say.
What Drives IPv6 Deployment?
What can we observe about the drivers for deployment of IPv6 in 2018?
You don’t have to be rich, but it helps.
You don’t have to be growing rapidly, but at times rapid growth provides sufficient grounds to make the move.
You don’t have to be desperately short of IPv4 addresses, but again it may help.
You can do it by yourself, but it can help when your competitors do it as well.
When we first designed the IPv6 protocol we through of the Internet in the same terms as the telephone network – as a peer network. Every connected device was meant to be able to both initiate transactions and respond to transaction requests. Addresses were both a network locator and a persistent endpoint identifier. When we were projected to run out of IPv4 addresses the consequence was that the network could no longer admit more endpoints.
That was then. Today is very different. These days it’s a client server network. Clients do not need persistent network-wide identity, and only need addresses as and when they communicate with servers. Servers do not need persistent identity either these days, as the identity of a server is a name-based distinguisher rather than an address-based identifier. We have positioned IP addresses in a different role, and no longer need to associate a unique public IP address with every connected endpoint. Address sharing technologies have allowed us to grow the pool of connected devices far beyond the number of unique addresses in the protocol.
How far can this client / server model grow while relying in IPv4?
How many devices can we cram into the IPv4 Internet before we break it?
Perhaps that’s a question we should not want to answer from experience.